Spectro CA-12 Battery Rapid-tester
"The electric light did not come from the continuous improvement of candles" [Oren Harari];
nor did faster horses lead to modern transportation [Henry Ford].
Spectro uses the method of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) to measure battery performance. This technology opens a new frontier in battery testing.
The Spectro CA-12 provides a complete battery state-of-health (SoH) assessment by evaluating SoC, CCA and capacity over a broad charge range. The CA-12 uses multi-model electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, an exclusive technology by Cadex.
U.S. patent 6,778,913
nor did faster horses lead to modern transportation [Henry Ford].
Spectro uses the method of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) to measure battery performance. This technology opens a new frontier in battery testing.
Spectro™ Battery Rapid-tester
The performance of a starter battery is governed by three symptoms: State-of-charge, CCA and capacity. A battery tester should reveal all three conditions, but here lays the difficulty: A good battery with low SoC performs alike a fully charged battery that is faded.The Spectro CA-12 provides a complete battery state-of-health (SoH) assessment by evaluating SoC, CCA and capacity over a broad charge range. The CA-12 uses multi-model electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, an exclusive technology by Cadex.
- The Spectro CA-12 is currently only available to Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEM) to integrate into warranty and after-market programs.
U.S. patent 6,778,913
Description
Why do Starter Batteries Fail?
| Mechanical | A mechanical defect is commonly diagnosed by physical inspection and a voltmeter. Batteries in trucks often fail due to shock and vibration. Plates short and cases crack. Replace the battery. |
| Heat-fail | Heat promotes corrosion that raises the internal resistance and slows cranking. The resulting drop in CCA can be measured with most automotive battery testers. A heat-fail battery does not die suddenly but gets gradually weaker and should be replaced. |
| Capacity-fade | Battery capacity drops unnoticed until the vehicle won’t start for lack of energy. Capacity and CCA readings don’t correlate; CCA can remain high while the capacity drops low gone. Start-stop, comfort-heating, and electric doors hasten capacity fade. A capacity of 40% estimates a remaining battery life of 6–12 months. Replace battery if lower. |
Definition of a Starter Battery
| SoC: | State-of-charge symbolizes the liquid levels as shown on the right. |
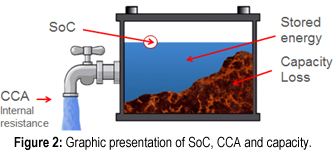 |
| CCA: | Cold Cranking Amp governs cranking simulated by a few- flowing tap. | |
| Capacity: | Energy storage capability in RC (Reserve capacity) or Ah. Loss is shown as rock buildup. |
What goes wrong?
Starter batteries should last 4–5 years in normal use. Figures 3 demonstrates early heat-fail; Figure 4 shows capacity-fade representing normal aging.|
Figure 3: Heat-fail. Battery failed early due to environmental conditions called heat-fail. |
|
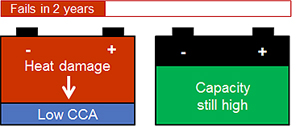 |
Symptoms: Rising internal resistance affects cranking ability that gets gradually worse. Test Method: Resistance tester to measure CCA. |
|
Figure 4. Capacity-fade. Battery deployed in a moderate climate fails mainly by capacity-fade. |
|
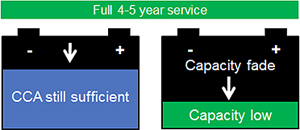 |
Symptoms: Capacity loss goes unnoticed, causing unexpected failure when low. Capacity should be checked as preventative service. Test Method: Evaluate battery with Spectro™ using EIS technology. |
CCA and Capacity on a two-dimensional Table
Starter battery supplies energy delivered at high current for cranking.
Figure 5: Battery performance based on CCA and capacity.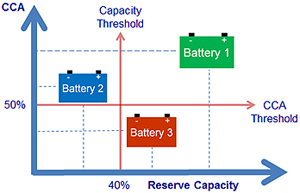 |
Battery 1: Good battery. Capacity and CCA are high. Battery 2: Defective battery. Low capacity but ample CCA. This is a common failure. Battery 3: Defective battery. Low CCA with ample capacity. This is less common. A battery tester must provide SoC, CCA and capacity. Capacity is the leading health indicator that predicts the end of battery life. CCA alone is inconclusive. |
Capacity is the Leading Health Indicator
To study failure modes, a luxury car maker in Europe tested 175 starter batteries. Mechanical and heat-fail batteries were eliminated before the test. Figure 6 demonstrates the aging trend.Most batteries pass through the Capacity Line on the left of the green field following the arrow. Very few batteries fail by dropping through the CCA Line.
Figure 6: Capacity and CCA of 175 aging AGM starter batteries.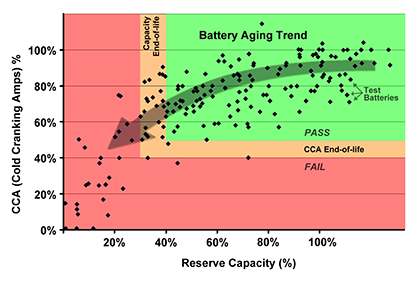 |
Most batteries pass through the Capacity Line; few fail because of low CCA. The test batteries were trunk mounted and driven in a moderate climate. Test Method: Capacity and CCA were tested according to DIN and IEC standards by an independent lab in Germany. |
Figure 7: Comparing CCA and capacity of 20 aging batteries.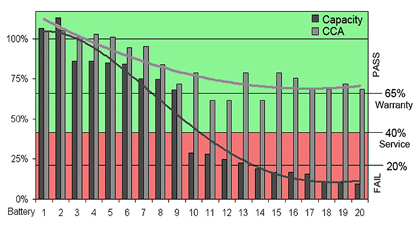 |
CCA of all batteries stays above 65% while the capacity of some batteries falls below 40%. Test Method: CCA was taken with Spectro CA-12; capacity was measured with an Agilent load bank by applying full discharges according to BCI standards. |
Test Snapshot
This failure analysis was taken in Europe. Tropical countries have different ratios.
| Ratio | Cause | Diagnostics |
|---|---|---|
| 48% | Capacity-fade | Active mass is worn out. |
| 23% | Low charge | City driving with ancillaries on. |
| 15% | No fault found | EIS adds depth to estimations. |
| 12% | Low CCA | Higher % in worm climates. |
| 1.5% | Mechanical | Shock and vibration. |
| 0.5% | Manufacturing defect | Most faults are user-induced. |
Testing is Simple
To test a starter battery, select between flooded or AGM and then enter CCA and capacity ratings in reserve capacity (RC) or ampere hours (Ah). The battery should have a minimal state-of-charge of 50%. The non-invasive test takes 15 seconds; the pass/fail threshold using a generic matrix is set to 40% or other setting specified. (Numeric capacity reading is available with a battery-specific matrix.)
Why EIS?
|
Long test times and manual evaluation restricted this technology to laboratory use in the past. Multi-model electro-chemical impedance spectroscopy (Spectro™) scans the battery with multiple frequencies and performs complex modeling to obtain capacity and CCA data. Cadex holds a patent on this technology. Battery testers based on AC conductance only see R1 of the Randle’s model in Figure 8; Spectro™ provides capacity by modelling R2 and C with matrices serving as lookup tables. |
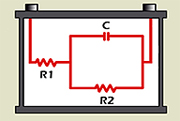 Figure 8: Randle’s model. R1 reflects resistance (CCA); R2 and C evaluate capacity. |
|
Scientists predict that the future of battery testing lays in EIS. Machine learning promises to expand the test range with high actuary. Cadex realizes the importance of battery diagnostics involving capacity and has been pioneering in EIS technologies since 2004. An analogy of advancement is the x-ray machine invented in 1895. While the X-ray only shows the outlines of a bone; the CAT scan also reveals soft tissues. Spectro™ with EIS provides this added information in a battery to enable accurate state-of-life predictions. |
|
Ordering Information
The Spectro CA-12 is currently only available to Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEM) to seamlessly integrate into warranty and after-market programs. Product inquiries should be directed to the following Cadex Automotive office locations:
-
America – Cadex HQ
[email protected]
-
Asia Pacific – Cadex Korea
[email protected]
-
Europe, Middle East, Africa – Cadex Europe
[email protected]
Cadex is continuously advancing Spectro™ in the form of improved battery diagnostics, broader test ranges, new battery types, and the distribution of test results. We are interested in your application and would be pleased to discuss your requirements.
Specifications
- Non-invasive hand-held rapid-tester for flooded, AGM, gel lead acid batteries, DC decoupled
- Injects 20–2,000Hz sinusoidal signal at 10mV
- Estimates reserve capacity (RC), internal resistance and CCA at a SoC range of 50–100%
- 15 seconds test time.
- Generic matrix sorts starter battery on a 40% capacity threshold or as specified.
- Reverse polarity and over-voltage protection
- Internal Li-ion battery provides ~150 tests per charge
| Range |
Resistance: 2–20mΩ Voltage: 12V, flooded & AGM |
| Test |
CCA: 100–1,200 RC: 60–210 minutes; 30–105Ah |
| Physical | 172 x 275 x 117mm (6.77” x 10.83" x .61"), 1.58kg (3.50 lbs.) |
| Ports | RS232, Bluetooth |
| Safety |
UL3101, CSA 1010, EN61010 EMI/ EMC: FCC part 15 Class A, EN55011 Level A, EN61000-6-3:2001 for EMC |
| Warranty | One (1) year against defects |